Algorithms
An algorithm is a well-defined set of steps for calculating or solving problems. Programming refers to a set of steps or procedures to solve a specific task or problem. It is expressed in a form that computers can understand and execute, enabling accurate and efficient problem solving. Algorithms are a fundamental concept in programming and are important in building learners' ability to think logically and respond appropriately to tasks. In programming, algorithms can be expressed using three basic control structures: sequencing, selection, and iteration.
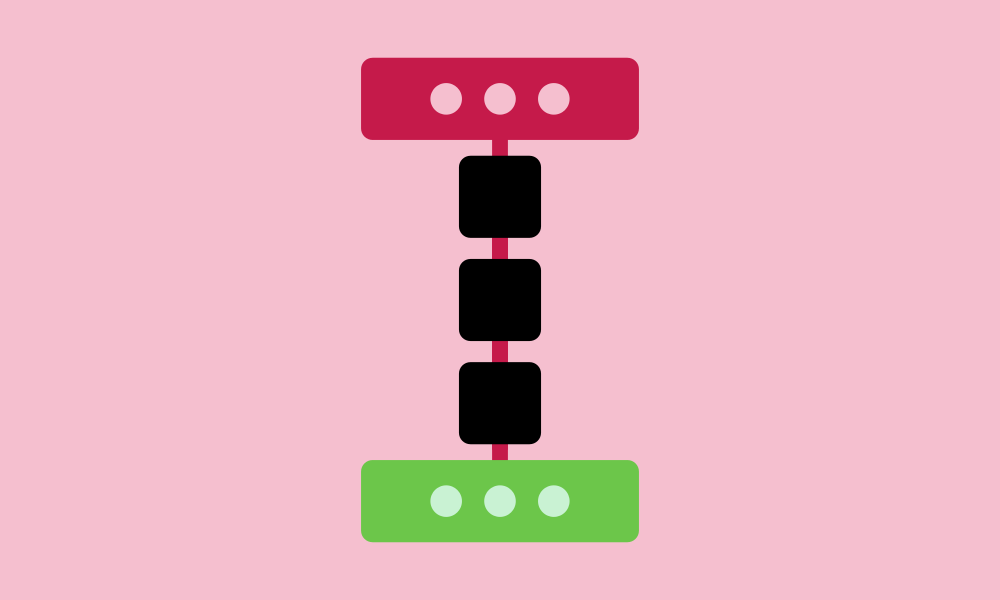
Sequencing
In programming, sequencing ensures that each step is executed in a specific order to achieve the desired results. Sequencing is a fundamental concept in programming, essential for learners to understand program logic and develop the ability to handle tasks appropriately.
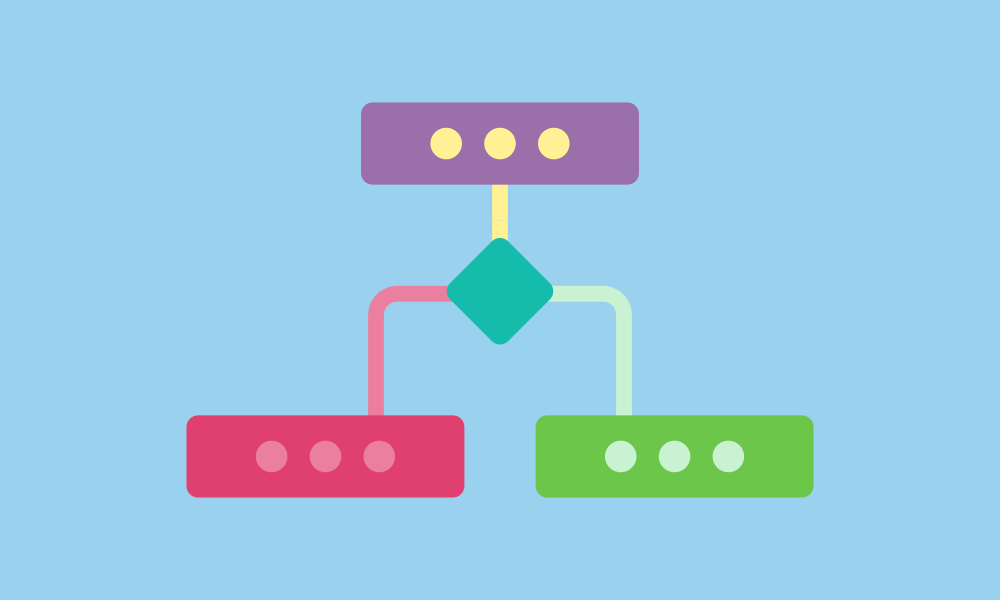
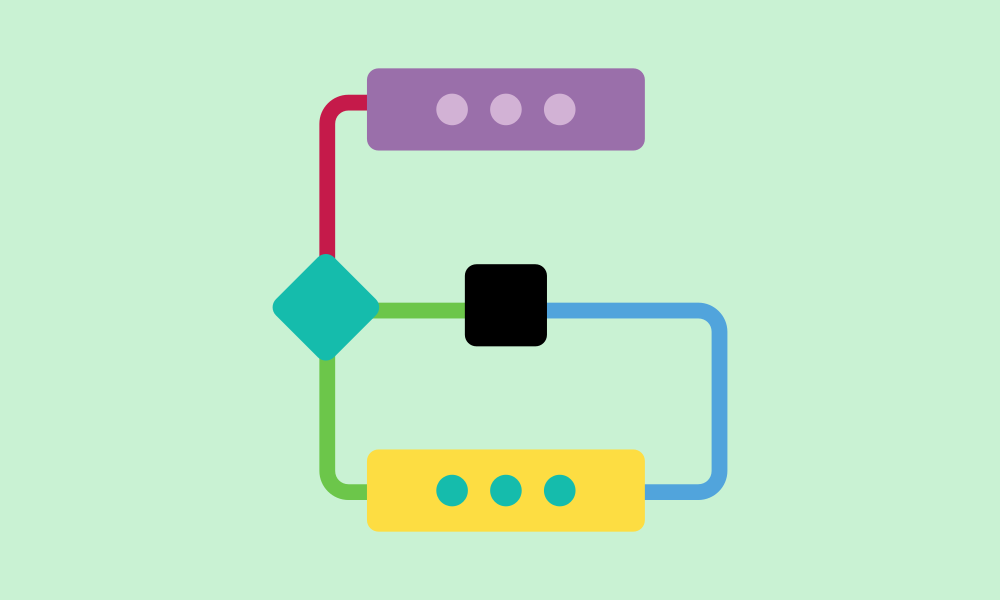
Selection
Also known as 'conditional branching', it allows programs to choose different paths based on whether certain conditions are true or false. The concept of selection provides an effective means for programs to address problems flexibly and dynamically.
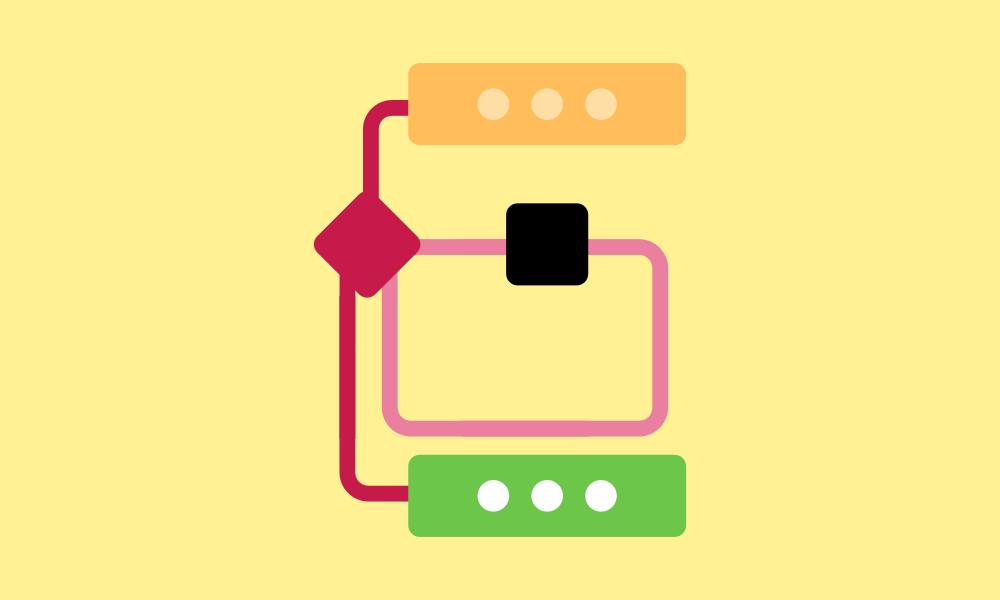
Iteration
Iteration in programming means doing the same thing over and over again. You might hear it called a 'loop'. It's like a repeat button: as long as certain conditions are met, it keeps doing the same block of instructions. This helps keep things tidy and saves time by not having to write the same stuff again and again. Using iteration in coding makes your programs more flexible and helps you tackle different kinds of problems.
User Interaction
User Interaction refers to the ability of a Scratch project to communicate with users, responding to their inputs and actions. In Scratch, various blocks can be used to program the project's response to keyboard inputs, mouse clicks, or other events. Introducing user interaction makes projects more engaging and user-friendly, allowing users to participate in creations such as animations, games, or stories.
Variables
In programming, variables are like containers for storing and changing information. They hold numbers, words, or other data, and you can do things like math or updates with them. For example, you can use variables to keep track of a score in a game or remember where something is. They're helpful tools that make programming more flexible and versatile.
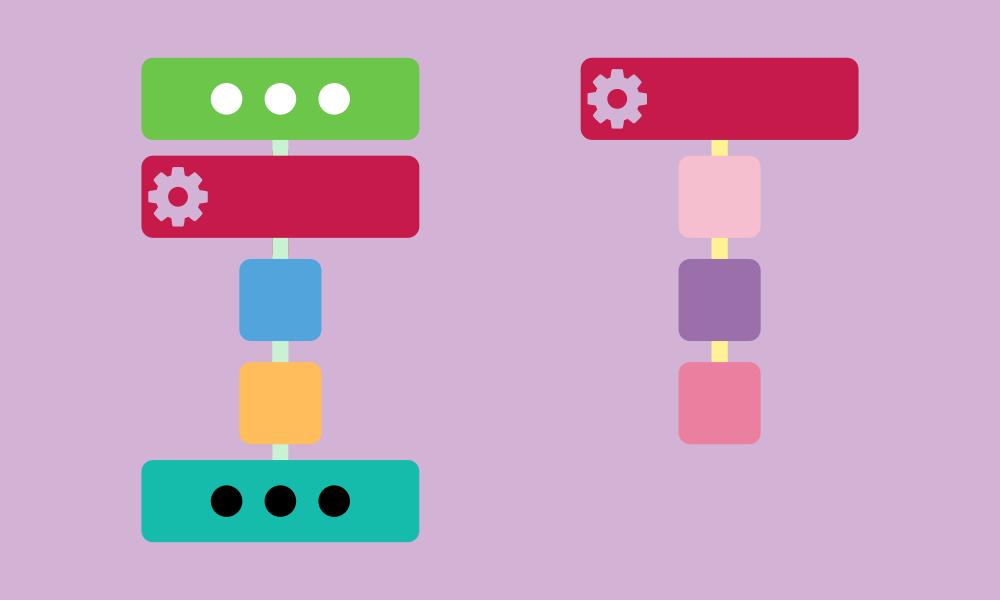
My Blocks (functions)
Functions (My Blocks) are a useful idea in Scratch projects. They let you use the same code over and over again. When you make a function, you can put several lines of code together into one block and use it many times in your project. For instance, you could create a function to do a certain action or calculation and use it whenever you need. This helps keep your program neat and makes it easier to handle big projects.
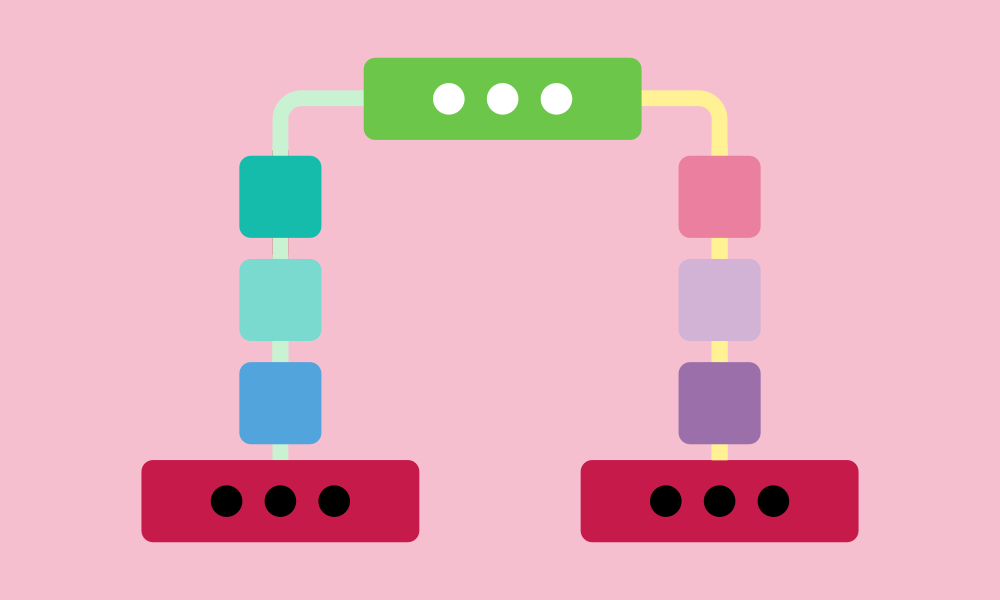
Parallelism
Parallel processing is when you do many things at once in programming projects. In Scratch, this happens by using different code blocks that work together at the same time. For example, it occurs when multiple characters move or when several events happen at once.
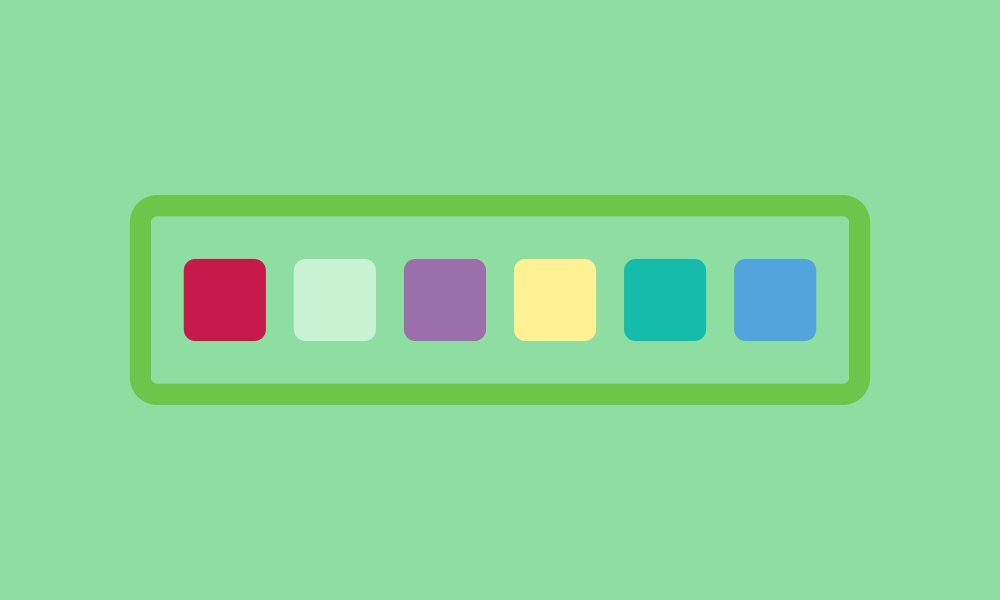

Data Structures
In programming, data structures help organize and manage information. In coding environments like Scratch, you can use lists or variables to structure different types of data. For example, this simplifies managing character positions or game scores. Understanding data structures improves program efficiency and simplifies handling complex tasks.
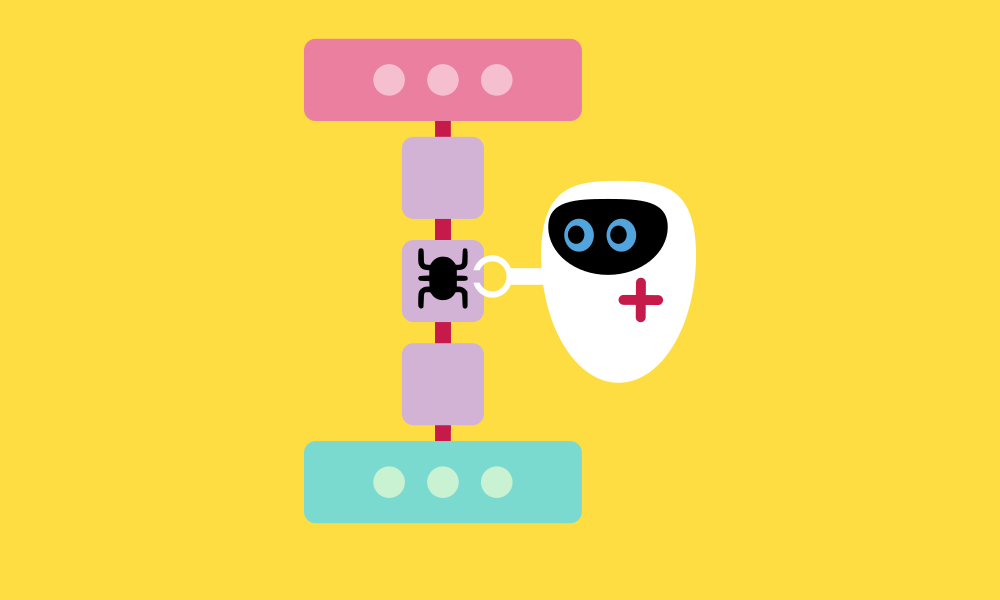
Debugging
Debugging is a process in programming. It involves identifying and fixing errors or issues within a program. In Scratch, debugging focuses on ensuring accurate placement of blocks and verifying conditions within the project. When errors occur, debugging involves identifying their causes and making appropriate corrections. Understanding debugging helps ensure smooth operation of the project and achieving the desired results.
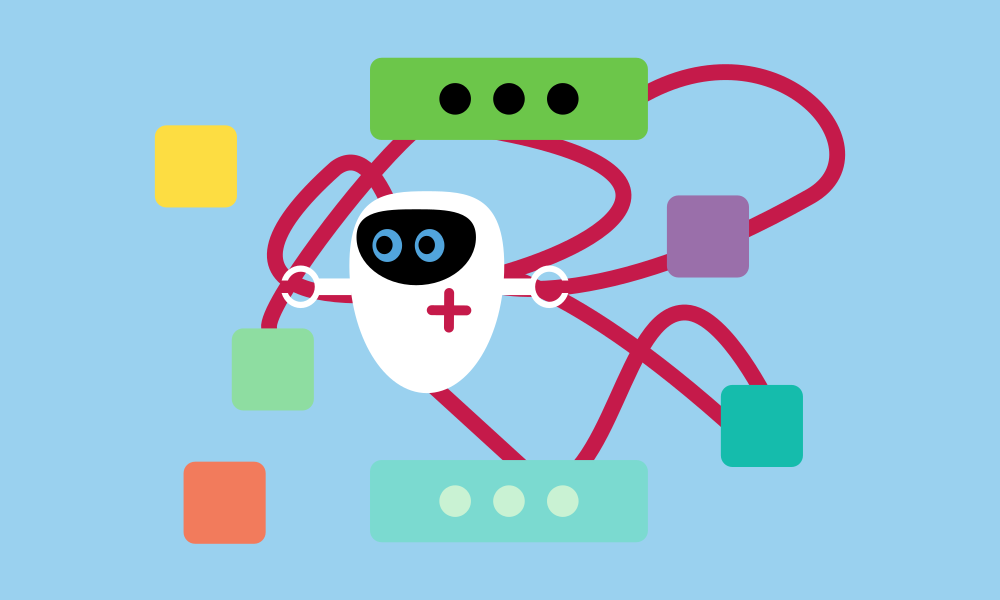
Code Organisation
Structuring code is a concept in programming. This involves organizing code to make it clear, understandable, and easy to maintain. By breaking code into smaller modules and functions, and grouping related parts together, an effective structure is created. This approach helps programs be more intuitively understood and adaptable to future changes.
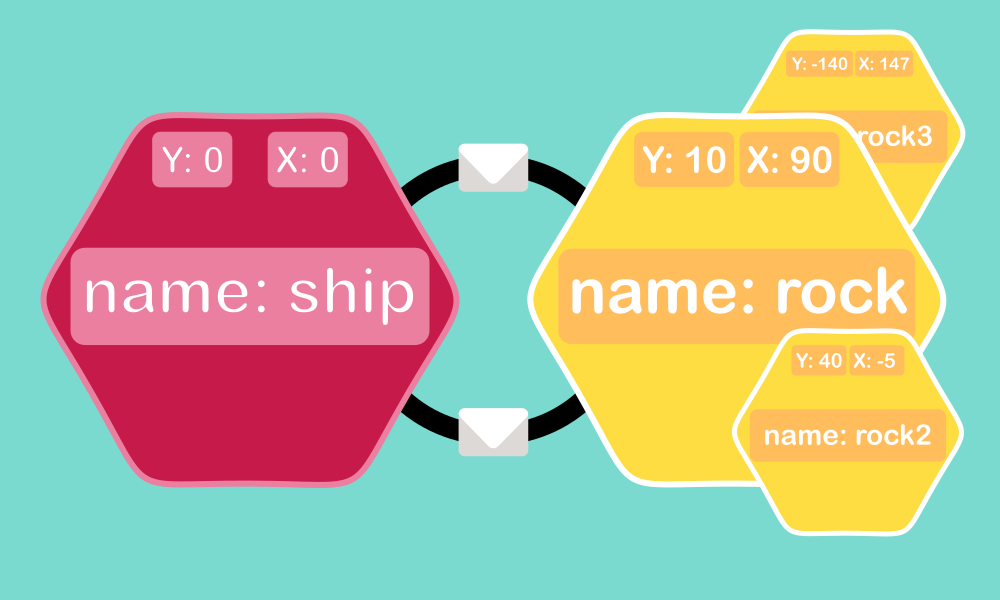
Object Oriented Programming (OOP)
In Object-Oriented Programming (OOP), an 'object' refers to something that does certain things and has certain qualities. In Scratch projects, things like sprites and clones act in their own special ways and have their own unique features. Think of each sprite or clone as a sort of character that can talk to others by sending and receiving messages. This helps show features of OOP like putting things in neat packages and making them interact with each other in Scratch projects.